L-1A visa requirements - who qualifies and how the intracompany transfer works
10 mins read | Mar 14, 2026
WHICH VISA TYPE IS BEST FOR YOU?
Contributor
Tukki
Reading time
5 mins read
Date published
Aug 23, 2024
No bureaucratic process is known for being easy or enjoyable, but understanding the steps that await us, how to approach them, and who to have by our side helps streamline the process.
Clarity and transparency are crucial for the beneficiary (i.e. the immigrant) as much as their legal team, but to date, no one tool or team has been able to provide this. That’s why we created Tukki — to combine the best of technology with lawyers — as well as this guide. There’s no reason why a comprehensive overview to assist you in making informed decisions should be hard to access.
Here, our focus will be on the most common nonimmigrant visa types that suit business owners and entrepreneurs primarily, so you can make sensible decisions about your future and your visa.
The E-2 visa is for investors, executives, and managers from treaty countries who invest significant capital in a U.S. enterprise. The L-1A visa is for managerial or executive employees being transferred to the U.S. from an international organization. The O-1A visa is for individuals with extraordinary ability in their field.
To overly simplify: the E-2 focuses on the investment, the L-1A on the company and the immigrant’s role within it, and the O-1A on the individual and their accomplishments.
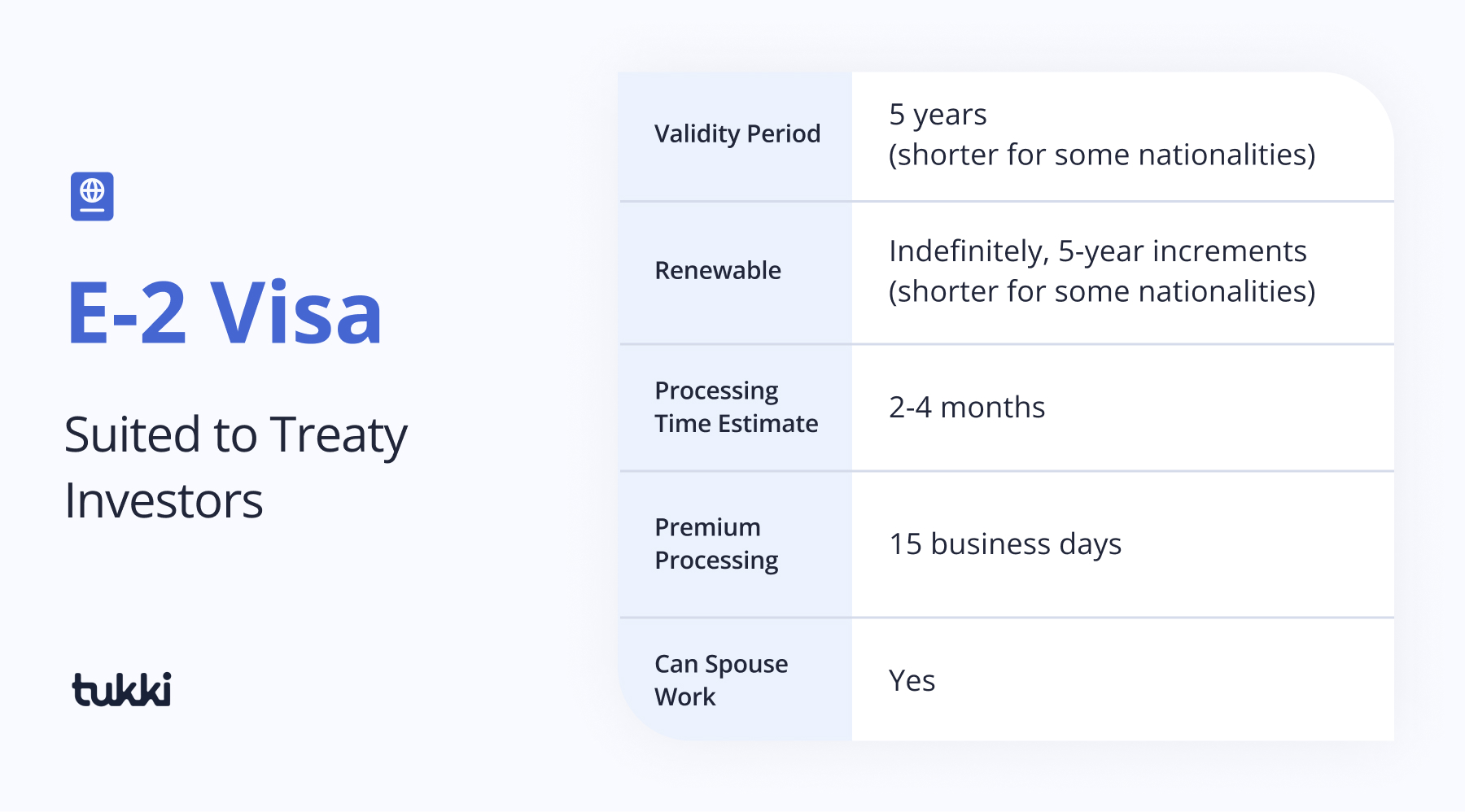
The E-2 visa caters to investors from treaty countries who invest significant capital in a US. enterprise.
Profiles that typically qualify: Entrepreneurs, business owners, investors
Sponsorship: Not required
Requirements:
Pros:
Cons:
L-1A visas are for managerial or executive employees being transferred to the US.
Profiles that typically qualify: Corporate executives, high-level managers, business owners
Sponsorship: Required
Requirements:
Pros:
Cons:

The O-1A visa is for individuals who have demonstrated extraordinary ability in their field, whether it’s science, education, business, or athletics.
Profiles that typically qualify: Entrepreneurs, industry experts, researchers, STEM professionals, athletes
Sponsorship: Required
Requirements:
Pros:
Cons:

In short, the E-2 visa is ideal for investors from treaty countries making substantial investments in US. businesses. The L-1A visa is suited for managerial or executive employees of multinational companies being transferred to the US. The O-1A visa caters to individuals with extraordinary abilities in various fields.
Each nonimmigrant US visa category offers unique benefits and challenges—choose the visa route that best aligns with your professional background and business objectives. By thoroughly understanding these nonimmigrant US visas, you can make an informed decision, facilitating your journey to work and thrive in the US. To continue the discovery journey, why not complete an assessment that will point you to your best US visa options?
WE CAN HELP
Need more clarity?
Find quick answers to frequent visa questions from our legal experts
How long can I stay in the U.S. on a TN visa?
Each TN admission allows you to stay for up to three years.
There's no maximum cumulative period, so you can renew your TN status indefinitely as long as you continue to qualify for the visa and maintain nonimmigrant intent.
This makes the TN a viable long-term work authorization option.
How much does an L-1A visa cost in total?
A standard employer filing an initial L-1A petition pays approximately $2,485 in government fees.
Adding premium processing brings the total to around $5,290 through February 2026, or $5,450 starting March 1, 2026.
Large employers subject to the Pub. L. 114-113 fee pay roughly $6,985 before premium processing.
Attorney fees and relocation costs are additional.
What is the success rate on immigration applications that Tukki worked on?
Tukki actively works with lawyers to assist with your visa applications and all of Tukki’s partner lawyers have success rates above 95% for client visa petitions.
What's the difference between an L-1A executive and a manager?
An L-1A manager either supervises professional or supervisory staff (personnel manager) or manages an essential function (function manager).
An L-1A executive directs the management of the organization or a major component, makes wide-latitude decisions with limited oversight, and establishes goals and policies.
The executive role requires broader authority and a higher position in the organizational hierarchy.
Can I switch from a tourist visa to a work visa while in the U.S.?
It’s possible through a change of status with USCIS, but officers may question your original intent when entering. Consular processing is often safer.
Other blogs for every step of your visa journey
L-1A visa requirements - who qualifies and how the intracompany transfer works
10 mins read | Mar 14, 2026
L-1A visa to green card - how the EB-1C pathway works and what to expect
8 mins read | Mar 10, 2026
Spouse work authorization in the U.S. - which visas allow your spouse to work?
7 mins read | Mar 9, 2026